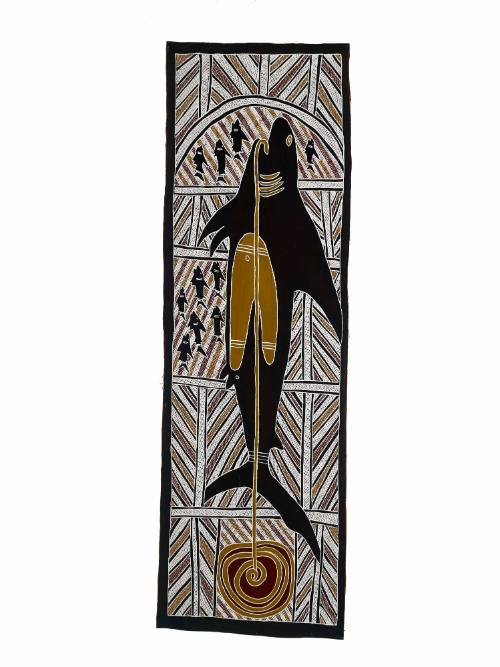
Mäna into Lutumba
Date1998
Object number00033810
NameBark painting
MediumNatural pigments on bark
DimensionsOverall: 1820 × 570 mm, 4.2 kg
Copyright© Minyapa Munuŋgurr
ClassificationsArt
Credit LineANMM Collection Purchased with the assistance of Stephen Grant of the GrantPirrie Gallery
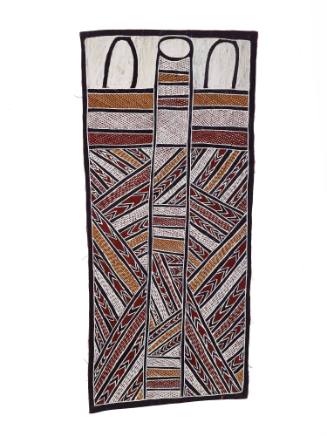
DescriptionThis painting shows Mäna the Ancestral shark with the sacred line uncoiling at the entrance to his domain. It represents the Yirritja moiety child within the body of the Dhuwa moiety. Mäna connects the other Dhuwa sea estates and carries its children into the sacred sandbar at Lutumba. The activities of Mäna are celebrated and reenacted in ritual, song and dance.HistoryThe Yolŋu people of Arnhem Land inhabit a landscape that was formed by the actions of ancestral beings, who can take both human and animal form. For instance water now flows where these creatures walked and hills have formed where they died. Ancestral Time is not just in the past but also the present and future. In light of this the sacred landscape and stories of East Arnhem Land are central to the Yolŋu people’s way of life and prominent themes in their bark paintings.
The Saltwater Project began in 1996 when an illegal fishing camp was discovered at Garranali, a sacred Aboriginal site in East Arnhem Land. This sacred area is home to the ancestral crocodile Bäru and found among the litter of the illegal camp was the severed head of a crocodile. This discovery prompted the local Yolnu people to produce a series of bark paintings that expressed the rules, philosophies and stories of their region. The project culminated in the production of 80 barks and allowed the Indigenous community to educate others about the social history, geography and personal stories of their traditional homeland. It also stressed the importance of Yolnu land ownership, laws and codes of behaviour for those who interacted with the landscape and sacred Indigenous places.
The Yolŋu have been involved in the land rights struggle since the 1960s. They are currently recognised as the traditional owners of northeast Arnhem Land under the Aboriginal Land Rights Act. This act was passed in the Northern Territory in 1976 and is seen as the benchmark in the recognition of Aboriginal land ownership in Australia. Despite this the issues of Indigenous land ownership, rights, customs and law continue to be contentious in the Australian legal system and wider community.SignificanceThis bark painting is representative of the people belonging to the Dhuwa moiety of the Djapu clan in the homeland of Wandawuy. It was painted for the Saltwater Project by the traditional owners of East Arnhem Land.