Plate VI. Nouvelle-Hollande
Artist
Charles Alexandre Lesueur
(1778-1846)
Engraver
Claude-Francois Fortier
(French, 1775 - 1835)
Date1807
Object number00030600
NameEngraving
MediumInk on paper
DimensionsOverall: 267 x 358 mm
ClassificationsArt
Credit LineANMM Collection Gift from Josef Lebovic Gallery
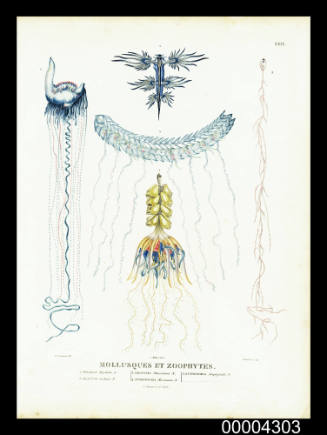
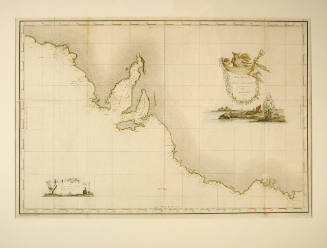
DescriptionA coloured engraving, plate VI from the account of Captain Nicolas Baudin's expedition 'Voyage de Decouertes aux Terres Australes'
In the Age of Sail coastal profiles were important aids to navigation, assisting mariners to recognise their location and determine their position along a specific coast. Profiles of the shore -coastal views- were usually taken from approximately three miles out to sea together with an annotation of the point of the compass from which the profile was drawn, e.g. 'appearance from East North-East'
HistoryNicolas Baudin sailed from France in October 1800 in command of the ships LE GEOGRAPHE and LA NATURALISTE on a scientific expedition to Australia. Baudin had previously served in the merchant marine, the French Navy (during the American War of Independence), the French East India Company and in the service of the Austro-Hungarian Emperor, Joseph II. He had established a good reputation as an amateur naturalist after returning from Puerto Rico with a splendid collection of natural history specimens in 1797.
Based on the success of the Puerto Rico expedition, Baudin proposed a scientific expedition to New Holland. In addition to achieving the scientific objectives of the expedition, Baudin planned to survey parts of the Australian coast - particularly those areas that were still poorly charted. The great French explorer Louis-Antoine de Bougainville was an influential supporter of the expedition and his son Hyacinthe de Bougainville served as a midshipman aboard LE GEOGRAPHE. Command of the LA NATURALISTE was by Lt. Cdr.Jacques-Felix Hamelin.
Although Baudin had been given overall command, he had had little control over the selection of the scientists and many of the officers; shipboard tensions that subsequently arose during the voyage were exacerbated by the expedition's very slow passage from France to Mauritius. Morale plummeted and consequently several disaffected officers left the expedition at Mauritius.
In May 1801 the expedition reached Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia. Baudin's instructions were to sail south to Tasmania, but with winter approaching, he chose instead to commence surveying north along the west Australian coast - discovering and naming Geographe Bay in the process. The GEOGRAPHE and NATURALISTE separated and Hamelin undertook a survey of Shark Bay, with the two ships reuniting some time later in Timor.
In November 1801 the expedition sailed south into the Indian Ocean and then east towards Van Diemen's Land (Tasmania) arriving there in January 1802. Over the next three months the expedition surveyed much of Bass Strait and the south coast of Australia. Baudin's survey coincided with that of Matthew Flinders in HMS INVESTIGATOR; an encounter between the two expeditions took place on 8 April 1802 at a place aptly named Encounter Bay. Although Flinders' charts have come to be accepted as the more detailed and accurate of the two, Baudin's work was published three years prior to Flinders' charts and offered the first comprehensive surveys of the Australian coastline.
Baudin's period in Tasmania produced a wealth of new geographical information; the expedition's scientists collected abundant natural history specimens and made important records of the indigenous Tasmanians (Peron produced a study of the Aborigines of Maria Island).
During the following year the expedition surveyed more of Bass Strait, King George's Sound, and the north coast of New Holland around Bathurst and Melville islands. In August 1803 the expedition returned to Mauritius where Baudin died on 16 September 1803.
As a result of Baudin's death, the expedition's charts were produced by Louis de Freycinet, the expedition's hydro- cartographical officer.
During the survey the GEOGRAPHE and NATURALISTE had mainly acted independantly of each other, but in 1802 Port Jackson was chosen as a place for a rendez-vous. At Port Jackson Baudin purchased a smaller vessel, the locally-built CASUARINA, to replace the slow and cumbersome NATURALISTE which was sent home to France. De Freycinet was given command of the CASUARINA.
SignificanceMade during Baudin's expedition, this set of coastal profiles is significant as one of the earliest detailed records of the Australian coastline; geographical features include Pieter Nuyts Land, Mount Gardner, Cape Leeuwin, Geographe Bay, Rottnest Island and Cape Lesueur.
Charles Alexandre Lesueur
1807
Charles Alexandre Lesueur
1807